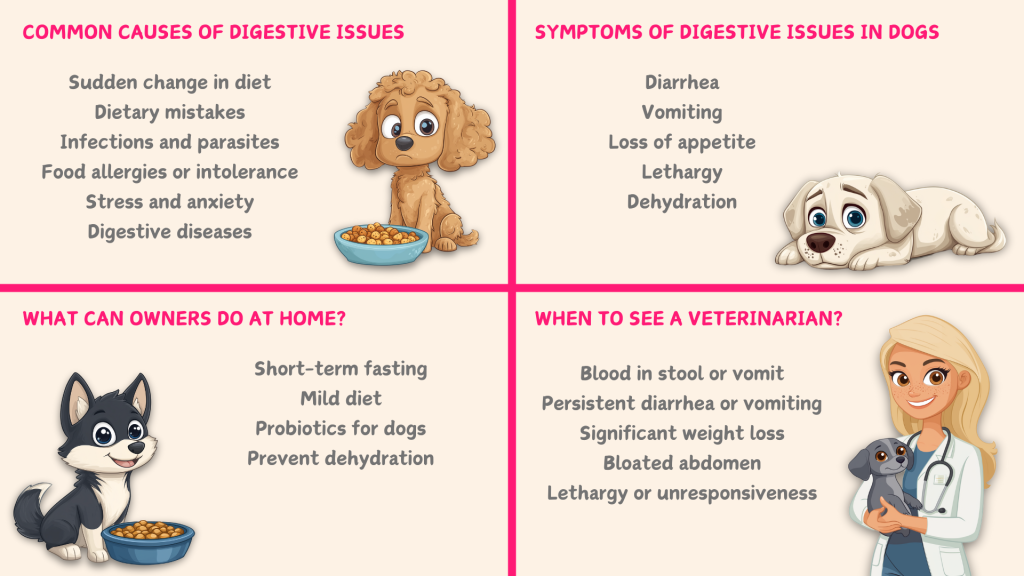
Digestive issues in dogs are common, but they are mostly manageable with proper care and quick action. Owners can assist with home care, but it is important to know when veterinary help is needed to prevent serious complications and ensure the health of our dog.